
By offering the Primary Years Programme of the International Baccalaureate, WIS continues the tradition of hundreds of schools across the globe, that have applied the best educational practices for decades. Our experience with the programme in the primary years at WIS has demonstrated that children are human sponges that can assimilate knowledge at a rapid pace. We have also learned that repetition of fundamental skills combined with a focus on exploring the human and physical world is a necessary condition for maximum learning. Read about our Learner Profile.
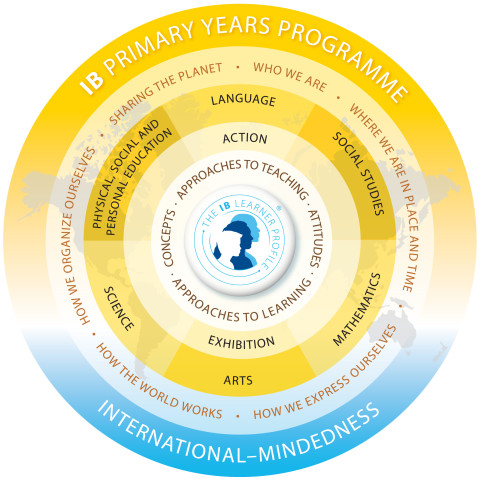
At the centre of the PYP curriculum are five essential elements: knowledge, concepts, skills, attitudes, and action. The aim of the programme is to help students acquire a holistic understanding of six main themes, shown on the outside of the programme model, through the interrelatedness of these essential elements. Read about PYP Subjects.
Knowledge: Transdisciplinary Themes
The programme is guided by a series of transdisciplinary themes which fit in with the different subject domains: Who we are, Where we are in time and place, How we express ourselves, How the world works, How we organize ourselves, Sharing the planet. From Early Years ages 5-6 until grade 5, students take part in 6 units of inquiry, one for each transdisciplinary theme. Early Years ages 3-4 and ages 4-5 take part in 4 rather than 6 units per year.
Concepts
Great importance is attached in all areas of the curriculum to the exploration of a core set of concepts: Form: What is it like?, Function: How does it work?, Causation: Why is it like it is?, Change: How is it changing?, Connection: How is it connected to other things?, Perspective: What are the points of view?, Responsibility: What is our responsibility? and Reflection: How do we know?
The concepts are presented in the form of key questions. It is these questions, used flexibly by teachers and students when planning an inquiry-based unit, which shape that unit and give it direction and purpose. It is in this sense that the key questions, and the concepts to which they relate, are said to drive the PYP curriculum.
Transdisciplinary Skills
The search for understanding is central to the belief of the PYP. The construction of meaning and, therefore, understanding is complemented by the students’ acquiring and applying a range of skills. These skills include:
- Social Skills: Accepting responsibility, respecting others, cooperating, resolving conflict, group decision making, adopting a variety of group roles;
- Research Skills: Formulating questions, observing, planning, collecting data, recording data, organizing data, interpreting data, presenting research findings;
- Communication Skills: Listening, speaking, reading, writing, viewing, presenting, non-verbal communication;
- Thinking Skills: Acquisition of knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, evaluation, dialectic thought, metacognition;
- Self-Management Skills: Gross motor skills, fine motor skills, spatial awareness, organization, time management, safety, healthy lifestyle, codes of behavior, informed choices.
Attitudes
While recognizing the importance of knowledge, concepts and skills, these alone do not make an internationally minded person. It is vital that there is also focus on the development of personal attitudes towards people, towards the environment and towards learning, attitudes that contribute to the well-being of the individual and of the group. In PYP schools, students should demonstrate: appreciation, commitment, confidence, cooperation, creativity, curiosity, empathy, enthusiasm, independence, integrity, respect and tolerance.
Action
An explicit expectation of the PYP is that successful inquiry will lead to responsible action, initiated by the children as a result of the learning process. This action may extend the child’s learning, or it may have a wider social impact, and will clearly look different within each age range.
Learning Design
Wherever possible, learning takes place within the units of inquiry, however certain parts of the curriculum (such as mathematics) require a specific focus. At the heart of the PYP is a commitment to structured inquiry as a method of teaching and learning. Students participate in problem solving, asking questions, actively seeking explanations, forming hypotheses and generalizations original to them.


